Your cart is currently empty!
First aid refers to the emergency or immediate care you should provide when a person is injured or ill until full medical treatment is available. For minor conditions, first aid care may be enough. For serious problems, first aid care should be continued until more advanced care becomes available.
The decision to act appropriately with first aid can mean the difference between life and death. Begin by introducing yourself to the injured or ill person. Explain that you are a first aid provider and are willing to help. The person must give you permission to help them; do not touch them until they agree to be helped. If you encounter a confused person or someone who is critically injured or ill, you can assume that they would want you to help them. This is known as “implied consent.
The first step in any emergency is the recognition of the problem and providing help. When in doubt or when someone is seriously injured or ill, you should always activate the emergency response system by calling 911 in the United States, or your own locality’s Emergency Medical Services (EMS) number. If you’re not sure how serious the situation is, the 911/EMS operator will ask you a series of questions to determine the severity of the situation.
Remain on the line until additional help arrives, or until the 911/EMS operator tells you to hang up. Emergency system dispatchers can guide you through the steps of performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), using an automated external defibrillator (AED), or delivering basic care until additional help arrives.
Whether you are at home, work, or school, know where the first aid kit and the AED are kept and be familiar with their contents. Know how to activate the Emergency Medical Services (EMS) in your area. Be aware of any policies in the workplace regarding medical emergencies.
After determining the problem, the next step in providing help is to determine the responsiveness of the injured or ill person. The best way to determine this is to tap the person and talk loudly to them: “Are you okay?” After determining responsiveness, yell for help. Look for any medical identifications, such as a necklace or a bracelet. This may provide a valuable clue to the cause of the situation.
Assessing the safety of the surroundings is critical when approaching any scene. You do not want to become another person who is injured or ill, so look for any potential dangers. Remove the person from any dangers, such as the presence of water at the scene. Be especially alert to avoid danger from automobile traffic.
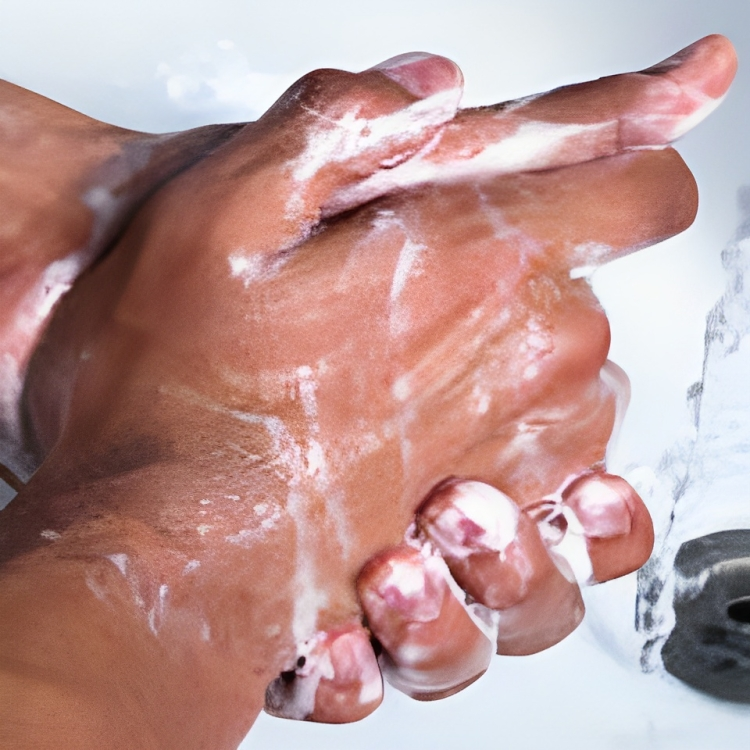
Handwashing is essential in the prevention of disease and illness. Wash your hands after each episode of care and after taking off gloves. When a sink is not available, use hand sanitizers. (Most hand sanitizers are alcohol-based and are a substitute for handwashing when needed.)

Using personal protective gear is an important strategy to minimize the risk of blood and bodily fluid exposure. If the person is bleeding, always wear gloves and protective eyewear when giving first aid care. The universal precaution is to use personal protective equipment whenever there is possible exposure to blood or bodily fluids; it reduces the risk for both the rescuer and the injured/ill person to be exposed to a blood-borne disease. Gloves protect your hands from exposure to blood and other bodily fluids, while eye protection prevents accidental exposure from splashing fluids.
Consider a pocket mask as part of your personal protective gear as it provides safety during rescue breathing. Be sure to dispose of all equipment that has touched bodily fluids in a biohazard bag when available.
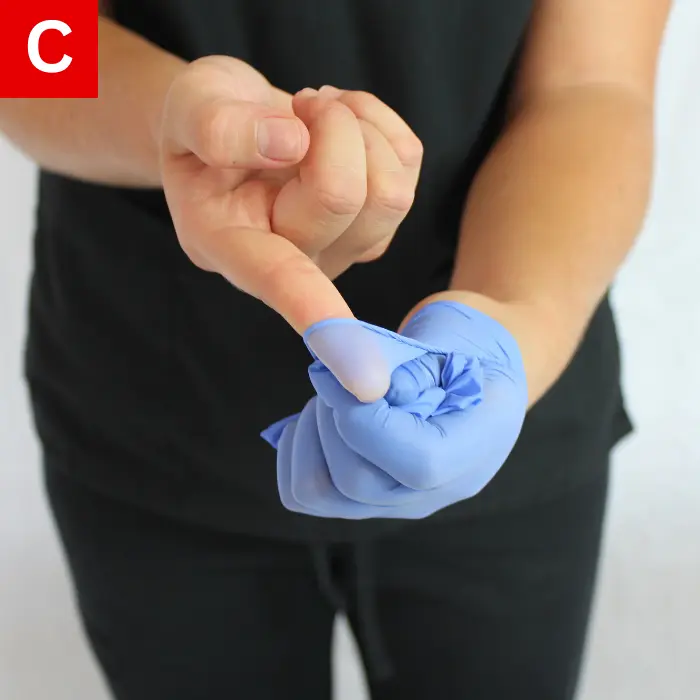
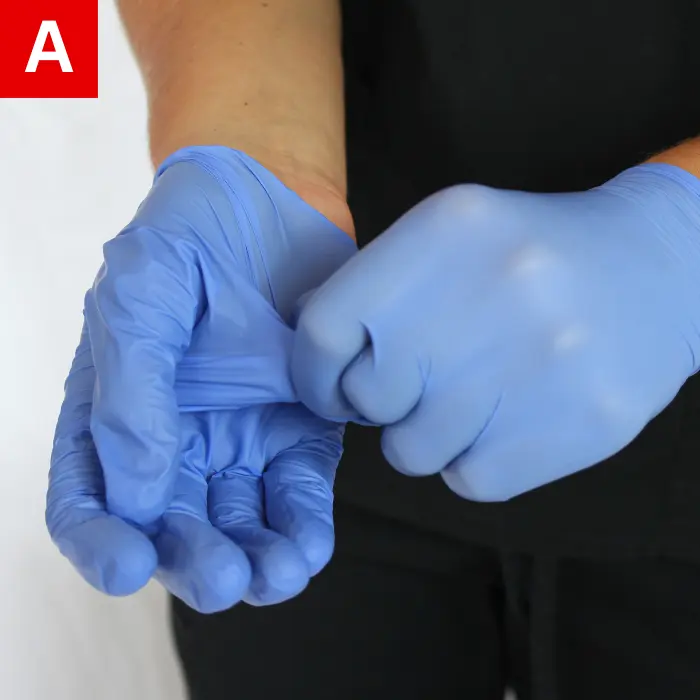
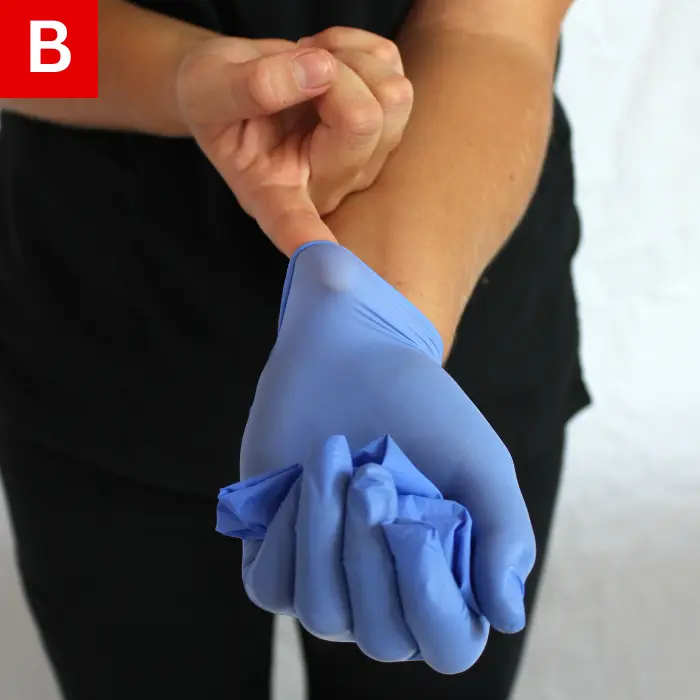

When taking off the gloves, avoid touching the outer contaminated surface. Slowly pull one glove off while turning it inside out (Figure 2a). Place the glove in the palm of the other gloved hand (Figure 2b), and then remove the second glove while turning it inside out (Figure 2c).
Consider purchasing a commercially available first aid kit or making your own. Having a kit in your home, your car, and at your place of work is essential to stay prepared.