Your cart is currently empty!
| INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS/FAILURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| AIRWAY | Open and support the airway | Suction | Consider advanced airway |
| BREATHING | Monitor O2 sats | Supplemental O2 | Nebulizers |
| CIRCULATION | Monitor vitals | Establish vascular access | |
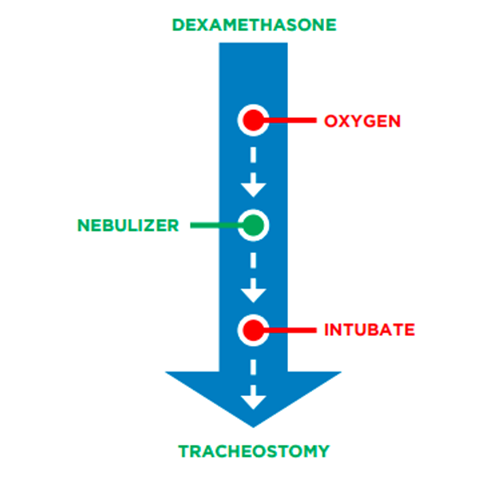
As an example, croup management depends on the severity of the disease.
Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, can cause hypertension and reduce activation of lymphocytes.No carotid artery pulse detected.
PALS management of respiratory distress/failure is adjusted based on the severity of the current condition. For example, mild asthma is treated with bronchodilator inhalers, but severe asthma (status asthmaticus) may require ET intubation. The provider must continually assess the person’s current needs and adjust care accordingly.
| UPPER AIRWAY | LOWER AIRWAY | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAUSE | TREATMENT | CAUSE | TREATMENT |
| CROUP |
| BRONCHIOLITIS |
|
| FOREIGN BODY |
| ASTHMA |
|
| ANAPHYLAXIS |
| ||
| LUNG TISSUE DISEASE | CNS ISSUES | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAUSE | TREATMENT | CAUSE | TREATMENT |
| PNEUMONIA |
| OVERDOSE |
|
| PNEUMONITIS |
| TRAUMA |
|
| PULMONARY EDEMA |
| ||
In general, providers commonly work from the least to the most
invasive intervention (top to bottom).If the person presents with severe distress, proceed directly to maneuvers that are more aggressive.
Albuterol is the most common medication used via nebulizer to cause bronchodilation.
Common causes of acute community-acquired pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumonia, Mycoplasma pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, and Chlamydia pneumonia.
High fever is the most common cause of quiet tachypnea.