Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
Effective cardiac arrest management improves patient survival rates and neurological outcomes. The ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm provides health care professionals with a structured approach to resuscitation efforts during these critical events. Understanding and implementing this algorithm is essential for anyone involved in advanced cardiac life support.
Importance of the ACLS Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
The ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm is designed to guide clinicians through a systematic process during a cardiac arrest scenario. It emphasizes the importance of high-quality CPR, early defibrillation, and the identification and treatment of reversible causes. By adhering to this algorithm, health care providers can ensure they deliver the most effective interventions at the right time.
Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
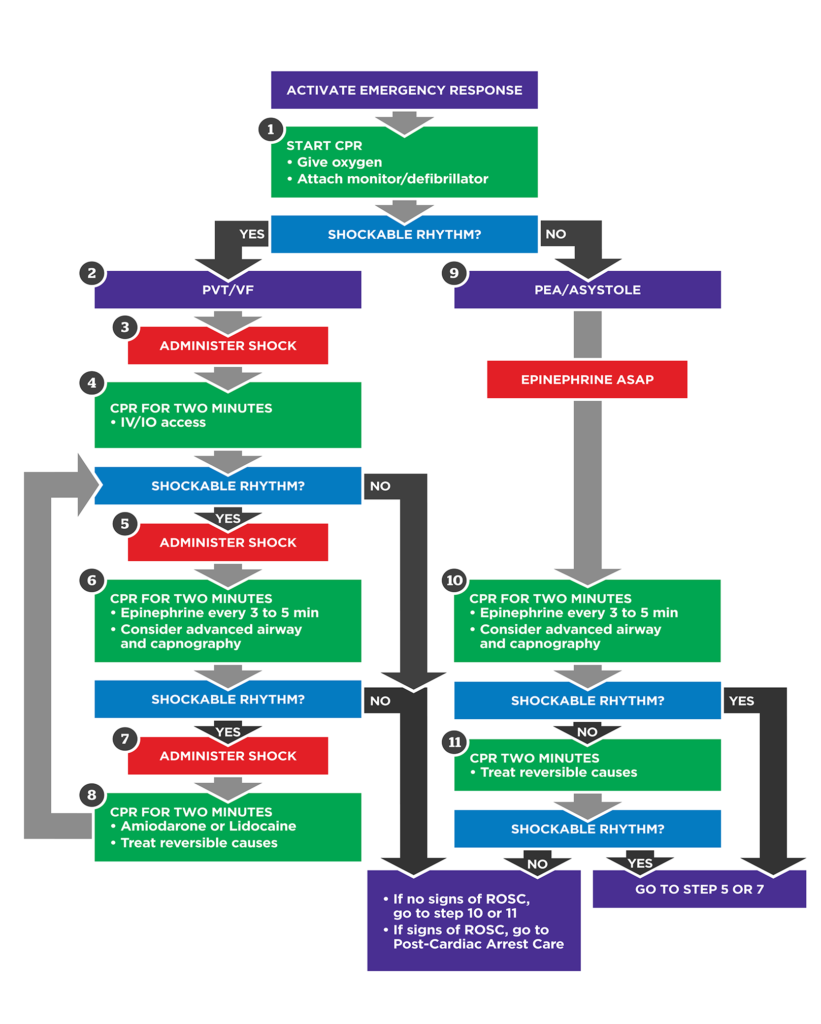
Key Components
While the specific steps are detailed in the existing content, it’s important to highlight the overarching components that make the ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm effective:
- High-Quality CPR: Maintaining optimal chest compression depth and rate, minimizing interruptions, and ensuring full chest recoil.
- Early Defibrillation: Prompt recognition of shockable rhythms and immediate defibrillation can significantly improve survival chances.
- Advanced Airway Management: Securing the airway to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation.
- Medication Administration: Appropriate use of medications like epinephrine and amiodarone, according to the algorithm.
- Reversible Causes: Identifying and addressing underlying causes (the H’s and T’s) that may have led to cardiac arrest.
CPR Quality
- Push hard (2-2.4″ (5-6 cm)) and fast (100-120 bpm) and allow chest recoil
- Minimize interruptions
- Do not over ventilate
- If no advanced airway, 30:2 compression to ventilation ratio
- Quantitative waveform capnography
- If ETCO2 <10 mmHg, attempt to improve CPR quality
Shock Energy
- Biphasic: Biphasic delivery of energy during defibrillation has been shown to be more effective than older monophasic waveforms. Follow manufacturer recommendation (e.g., initial dose of 120 to 200 J); if unknown, use maximum available. Second and subsequent doses should be equivalent and higher doses should be considered.
- Monophasic: 360 J
Return of Spontaneous Circulation
- Return of pulse and blood pressure
- Sudden sustained increase in PETCO2 (typically ≥ 40 mmHg)
- Spontaneous arterial pressure waves with intra-arterial monitoring
Advanced Airway
- Supraglottic advanced airway or ET intubation
- Absolute placement confirmation:
1. Negative Epigastric Auscultation
2. Positive Bilateral Chest Auscultation
3. Vocal Cord Visualization
4. Quantitative ETCO2
- 10 breaths per minute with continuous chest compressions
Drug Therapy
- Epinephrine IV/IO Dose: 1 mg, administer as soon as possible then every 3 to 5 minutes after
- Amiodarone IV/IO Dose: first dose is 300 mg bolus, second dose is 150 mg
- Lidocaine: 1st dose: 1-1.5 mg/kg, second dose: 0.5-0.75 mg/kg
Reversible Causes
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- H+(acidosis)
- Hypothermia
- Hypo-/hyperkalemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Tamponade, cardiac
- Toxins
- Tension pneumothorax
- Thrombosis, pulmonary or coronary
- Trauma
Enhancing Resuscitation Efforts
Implementing the ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm effectively requires teamwork, clear communication, and regular practice. Health care professionals should continue education and simulation training to improve these life-saving skills.
Team Dynamics and Communication
- Role Assignment: Clearly define team member roles during resuscitation.
- Closed-Loop Communication: Confirm orders and interventions to prevent errors.
- Leadership: Effective team leaders guide resuscitation efforts smoothly, ensuring adherence to the ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm.
Continuing Education and Certification
Staying current with the latest guidelines is crucial. Our Online ACLS Certification Course provides comprehensive ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm training, ensuring health care providers have the most up-to-date knowledge and skills.
Course Benefits
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers all aspects of ACLS, including cardiac arrest management.
- Flexible Learning: Access course materials anytime, anywhere.
- Accredited Certification: Earn a certification recognized by health care institutions nationwide.
- Immediate Results: Receive your digital certificate upon successful completion.
- Continuing Education Credits: Fulfill professional development requirements.
Commitment to Excellence in Cardiac Care
Mastering the ACLS adult cardiac arrest algorithm is vital in providing high-quality emergency care. By integrating this algorithm into practice, health care professionals can significantly impact patient outcomes during cardiac arrest events.




