Adult Immediate Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
Effective management following the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) is crucial for improving the survival and neurological outcomes of patients who have experienced cardiac arrest. Understanding and implementing the ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm is essential for health care professionals involved in resuscitation and critical care. This guide provides an overview of the key aspects of the ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm, enhancing your ability to deliver optimal care during this critical phase.
Importance of the ACLS Adult Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
The ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm is a systematic approach designed to stabilize patients after ROSC, minimize brain injury, and prevent the recurrence of cardiac arrest.. It emphasizes:
- Optimizing Hemodynamic Stability: Maintaining adequate blood pressure and cardiac output.
- Ensuring Adequate Oxygenation and Ventilation: Preventing hypoxia and hyperoxia.
- Controlling Temperature: Implementing targeted temperature management (TTM) to improve neurological outcomes.
- Monitoring and Treating Underlying Causes: Identifying and managing precipitating factors.
By adhering to the ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Adult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
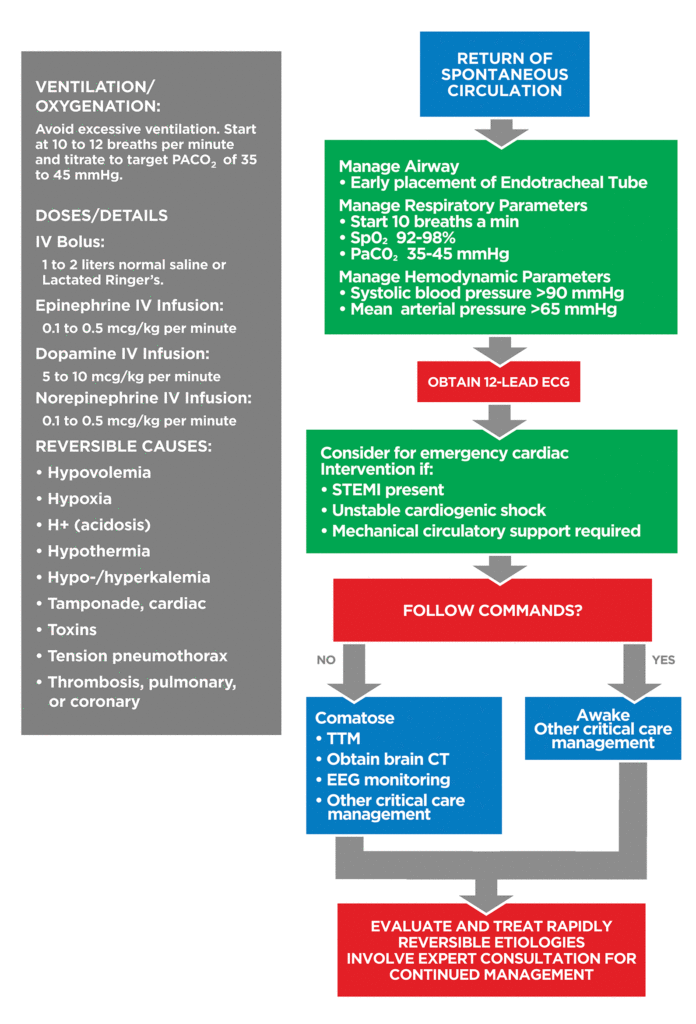
Key Components of the ACLS Adult Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
1. Airway and Breathing
- Secure the Airway: Consider endotracheal intubation if not already performed.
- Optimize Ventilation: Aim for an oxygen saturation of 94-99%. Avoid excessive ventilation; target a respiratory rate to achieve a PaCO₂ of 35-45 mm Hg.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use waveform capnography to confirm proper endotracheal tube placement and monitor ventilation.
2. Circulation
- Blood Pressure Management: Maintain a systolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or mean arterial pressure (MAP) ≥65 mm Hg using fluids and vasopressors as needed.
- IV/IO Access: Ensure reliable intravenous or intraosseous access for medication administration.
- 12-Lead ECG: Obtain an assessment for STEMI or other arrhythmias requiring intervention.
3. Temperature Control
- Temperature Control: Initiate TTM for comatose patients by cooling to 32-37.5°C for at least 24 hours.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor core temperature using esophageal or bladder.
4. Neurological Assessment
- Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): Regularly assess neurological status.
- Pupil Response: Check for reactive pupils.
- Consider Neurology Consultation: For persistent coma or seizures.
5. Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests
- Blood Tests: Check electrolytes, glucose, and other pertinent labs.
- Chest x-ray: Evaluate for pulmonary complications or confirm tube placements.
- Echocardiogram: Assess cardiac function if indicated.
6. Treat Underlying Causes
- Identify Precipitating Factors: Use the H’s and T’s mnemonic to consider reversible causes such as hypoxia, hypovolemia, thrombosis, toxins, tension pneumothorax, etc.
- Coronary Reperfusion: For patients with STEMI or suspected myocardial infarction, proceed with reperfusion therapy as appropriate.
Enhance Your Skills with Our Online ACLS Certification Course
Continuous education and practice are essential to effectively apply the ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm. Enroll in our Online ACLS Certification Course to:
- Deepen Your Knowledge: Comprehensive modules covering all Advanced Cardiac Life Support aspects, including post-cardiac arrest care.
- Improve Competency: Interactive scenarios to practice critical decision-making.
- Earn Accreditation: Receive a certification recognized by health care institutions nationwide.
- Flexible Learning: Study at your own pace with 24/7 access to course materials.
- Immediate Certification: Obtain your digital certificate upon successful completion.
Commitment to Excellence in Post-Cardiac Arrest Care
Mastering the ACLS adult post-cardiac arrest care algorithm empowers health care professionals to deliver lifesaving interventions confidently. By staying current with the latest guidelines and refining your skills, you contribute to better patient outcomes and demonstrate your dedication to high-quality emergency care.




