ACLS Rhythms and Interpretation
Understanding and accurately interpreting ACLS rhythms is critical for health care professionals involved in advanced cardiac life support. Proficiency in this area enables timely identification of life-threatening arrhythmias and guides appropriate interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes during cardiac emergencies.
Importance of Mastering ACLS Rhythms
- Rapid Recognition: Quickly identifying ACLS rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, asystole, and pulseless electrical activity is essential for initiating the correct treatment protocols.
- Effective Intervention: Knowledge of ACLS rhythms ensures that health care providers can administer the appropriate medications and therapies in accordance with the latest guidelines.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Accurate interpretation of ACLS rhythms contributes to higher survival rates and better neurological outcomes for cardiac event patients.
STEP 1: RECAP THE PQRST PROPERTIES
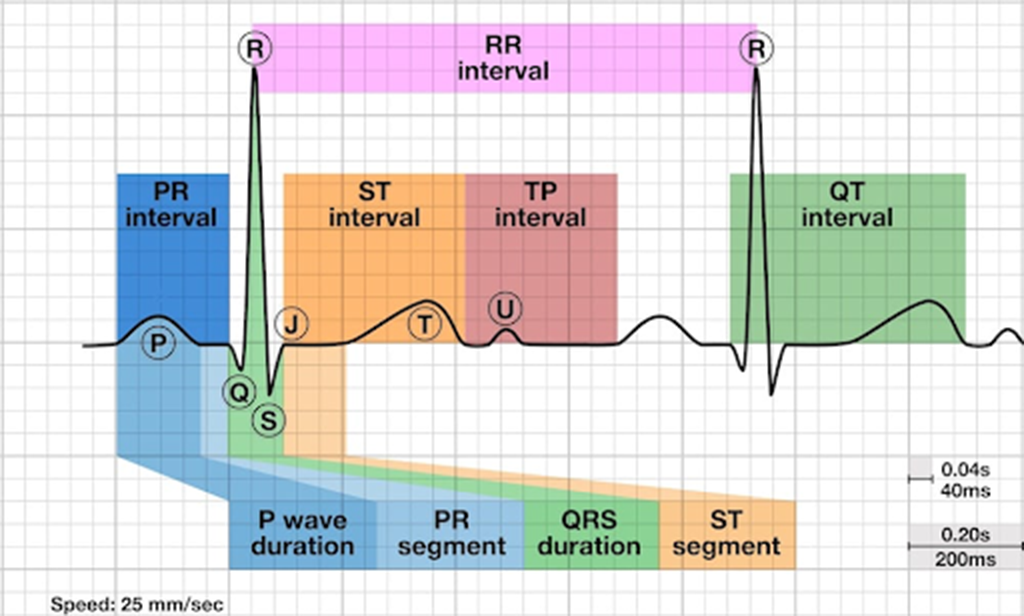
| PROTOTYPICAL ECG TRACING | |
|---|---|
| P-wave | Electrical activity is traveling through the atria. Synonymous with atrial depolarization. Reflects atrial contraction. |
| QRS Complex | Electrical activity is traveling through the ventricles. Depolarization of the left and right ventricles. Reflects ventricular contraction. |
| T-wave | Synonymous with ventricular repolarization. Reflects the start of ventricular relaxation. |
| PR Interval | Onset of the P-wave to the start of the QRS complex. Reflects conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node. |
| PR Segment | End of the P-wave to the start of the QRS complex. Reflects time delay between atrial and ventricular activation. |
| ST Interval | Onset of the S-wave to the start of the T-wave. Reflects initial, slow phase of ventricular repolarization. |
| ST Segment | End of the S-wave (J point) to the start of the T-wave. Reflects ventricular repolarization. |
| QT Interval | Onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. Reflects the period between ventricular depolarization and ventricular repolarization. |
| TP Interval | The TP segment is the portion of the ECG from the end of the T wave to the beginning of the P wave |
| RR Interval | Reflects time elapsed between two successive R-waves of the QRS. |
STEP 2: IDENTIFY THE COMMON CATEGORIES OF ACLS RHYTHMS WITH A FEW EXAMPLES
Sinus Rhythms:
- Normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
- Sinus bradycardia
- Sinus tachycardia
Bradyarrhythmia and Conduction Blocks:
- 1st degree AV block
- 2nd degree AV block Type I (Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach’s)
- 2nd degree AV block Type II (Mobitz Type II)
- 3rd degree AV block (complete heart block, CHB)
Tachyarrhythmias:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
- Wide-complex tachycardias.
Pulseless Rhythms:
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vTach)
- Ventricular fibrillation (vFib)
- Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
- Asystole
Atrial Dysrhythmias:
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial fibrillation (aFib)
STEP 3: IDENTIFY THE MOST COMMON ACLS RHYTHMS
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: 60-100 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment: None
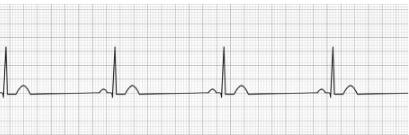
Sinus Bradycardia
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: <60 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment (Symptomatic): Atropine, Dopamine (infusion), Epinephrine (infusion)
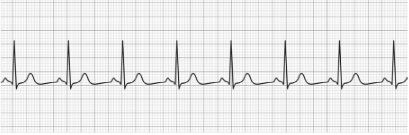
Sinus Tachycardia
- Normal P-wave
- Normal QRS Complex
- Normal T-wave
- HR: >100 BPM (at rest)
- Treatment: Reverse underlying condition (fever, anxiety, exercise), beta-blockers (metoprolol, sotalol)
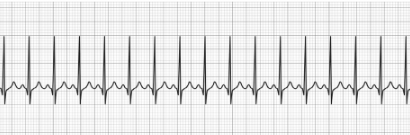
1st Degree Heart Block
- Prolonged PR interval due to delay in AV signal transmission
- P-wave may be buried in the preceding T-wave
- Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing (only indicated if prolongation of the PR interval is >400 ms)
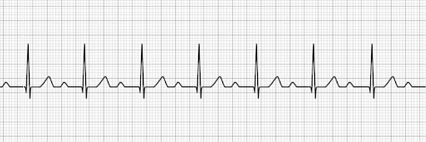
2nd Degree AV Block Type I (Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach’s)
- Progressive lengthening of the PR interval
- Progression occurs until the QRS complex is dropped
- Treatment: Atropine, Dopamine, Transcutaneous pacing
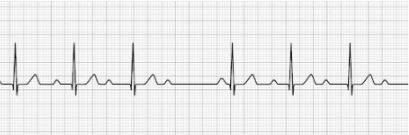
2nd Degree AV Block Type II (Mobitz Type II)
- PR interval is > 0.20 seconds and consistent (not gradually getting longer) but drops a beat,
generally on a pattern of 3:1 or 4:1 - Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing
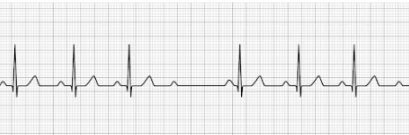
3rd Degree AV Block (complete heart block, CHB)
- No identifiable relationship between the P-wave and QRS waves
- P-P intervals are normal but do not relate to the QRS complex
- Treatment: Transcutaneous pacing
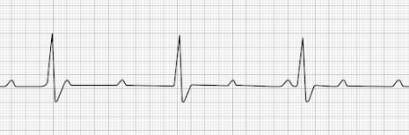
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Profoundly rapid atrial rhythm with narrow QRS complexes
- Occurs when the signal impulse originates over the bundle branches
- HR: 150-250 BPM
- Treatment: Vagal maneuvers, Adenosine, synchronized cardioversion
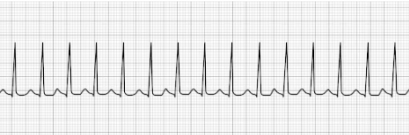
Atrial Fibrillation (aFib)
- Uniquely characterized by an absence of P-waves before the QRS complex
- HR: Highly irregular with significant fluctuation
- Treatment: beta-blockers (Metoprolol, Sotalol, etc.), Ca++ channel blockers (Diltiazem, Verapamil, etc.), Digoxin, synchronized cardioversion.
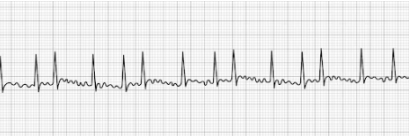
Atrial Flutter
- Uniquely characterized by a saw-toothed flutter appearance
- Toothed fluttering represents multiple P-waves for a single QRS complex
- Treatment: synchronized cardioversion, beta-blockers (Metoprolol, Sotalol, etc.),
Ca++ channel blockers (Diltiazem, Verapamil, etc).
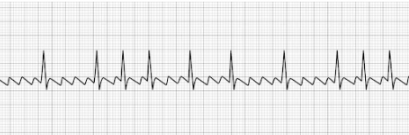
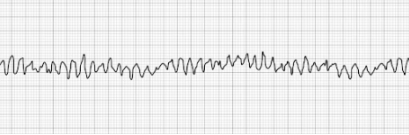
Ventricular Tachycardia (vTach)
- Abnormally-patterned wide QRS complex
- No P-waves
- High likelihood of rapid deterioration to a state of ventricular fibrillation
(vFib) - Often responsive to electrical defibrillation
- HR: >100 BPM
- Treatment: Defibrillation
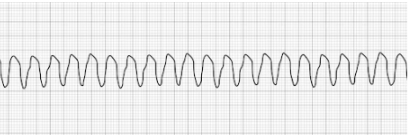
Pulseless Ventricular Fibrillation (vFib)
- Characterized by a chaotic and disorganized wave pattern
- Patient has no palpable pulse
- Treatment: Defibrillation, epinephrine, amiodarone, lidocaine HCl
Tips for Enhancing ACLS Rhythm Interpretation Skills
- Regular Practice: Engage in continuous education and practice ECG interpretation to become more familiar with various ACLS rhythms.
- Utilize Resources: Leverage educational materials, such as textbooks, online courses, and simulation tools focused on ACLS rhythms.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest ACLS guidelines and recommendations to ensure your knowledge of ACLS rhythms is current.
Enhance Your Skills with Our Online ACLS Certification Course
To further develop your proficiency in interpreting ACLS rhythms, consider enrolling in our Online ACLS Certification Course. This comprehensive course offers:
- In-Depth Learning: Detailed modules covering all essential ACLS rhythms and their clinical significance.
- Interactive Content: Engaging lessons with practice ECGs to help solidify your understanding of various rhythms.
- Flexible Access: 24/7 online availability allows you to learn quickly.
- Accredited Certification: Receive a nationally recognized certification upon successful completion.
- Immediate Results: Obtain your digital certificate and provider card instantly after passing the exam.
Commitment to Excellence in Cardiac Care
By mastering ACLS rhythms, you position yourself as a competent and confident health care provider capable of making critical decisions during cardiac emergencies. Invest in your professional development to enhance patient care and outcomes.




